02.04.11
The Groundhog Day Tropical Storm of 1952
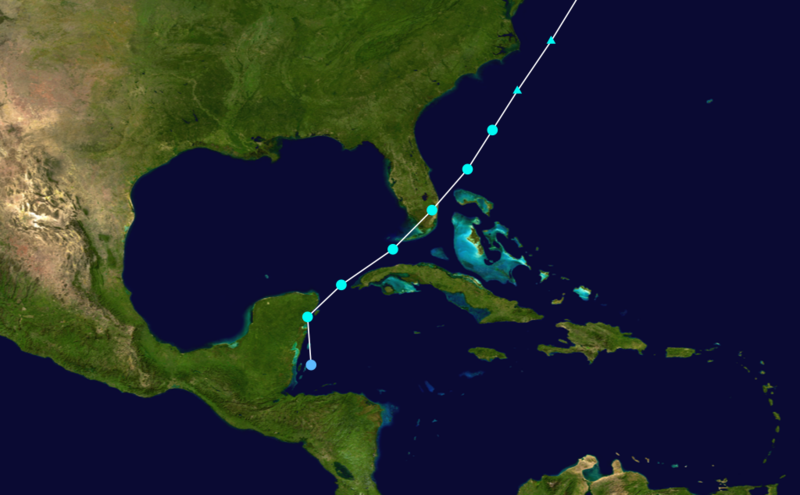
Groundhog Day, 1952: a rare tropical storm formed in the western Caribbean. The tropical cyclone quickly moved north-northwestward, and passed by Cancún before turning northeastward and tracking across the northwest coast of Cuba.
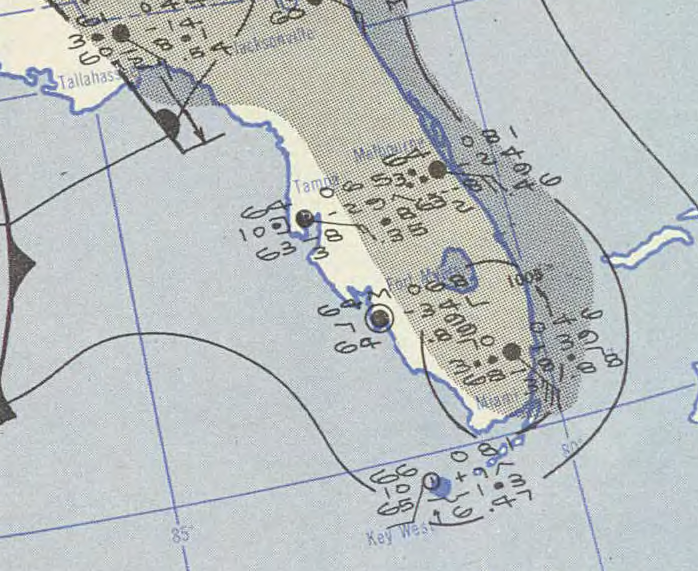
Early the next day, on February 3rd, the tropical storm struck Key West and then made landfall again near Cape Sable, in southern Florida. The Miami National Weather Service office reported a wind gust of 68 mph (110 kph) and a minimum pressure of 1004 mb. There was no serious damage or injuries, though some crops and power lines in southern Florida sustained some damage and 2 to 4 inches of rain fell along the storm’s path.
This tropical storm remains the only tropical cyclone to exist in the Atlantic in February in recorded history.
U.S. Weather Bureau (NWS predecessor) surface map on February 2, 1952
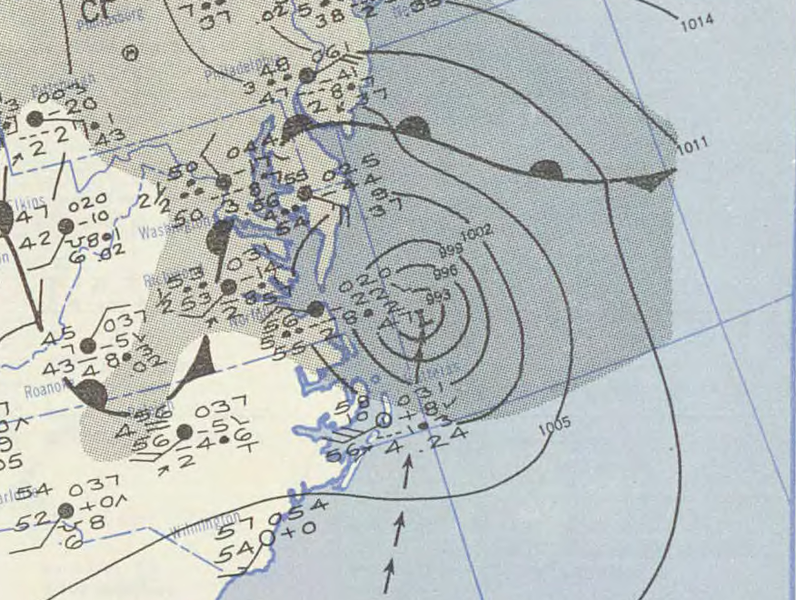
After the tropical storm went back to sea, it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone with maximum winds of 85 mph (140 kph) and waves up to 35 feet off the North Carolina coast on the 4th. The cyclone later moved past Cape Cod before coming ashore in Maine on the 5th. Damage included a freighter off the Outer Banks that washed ashore when water entered the fuel line and damaged the engine (the crew was all rescued by the Coast Guard), some downed power poles and tree limbs in the Northeast, and minor power outages.
U.S. Weather Bureau surface map on February 4, 1952
The tropical storm was very unusual, and it was initially left out of the official tropical cyclone database. Had it been included right away, the storm’s name would have been Tropical Storm Abel.
Source for much of the information and figures: Wikipedia