12.28.10
Posted in Non-US Weather, Weather News at 8:01 am by Rebekah
This week’s post in the global weather and climate series features Yogyakarta, Java, in Indonesia.
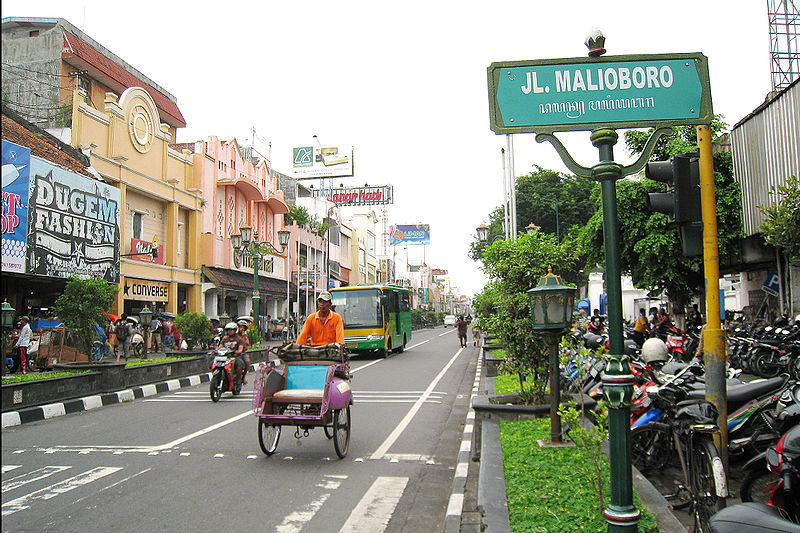

Jalan Malioboro, the most famous street in Yogyakarta for shopping and dining. Courtesy of Wikipedia.
Yogyakarta (or Jogjakarta) is a city of about 637,000 people in an area of 12.5 square miles. The city is found on the south central coast of Java, the 5th largest island in Indonesia (13th largest in the world, with a size of 51,000 square miles) and the most populated island in the world (136+ million). Situated on this volcanic island, Yogyakarta is prone to frequent earthquakes and occasional volcanic eruptions from nearby Mount Merapi.
Yogyakarta was established in 1756, under the Islamic Sultanate of Mataram. In the 1800s, the region fell into the hands of the Dutch. During the Indonesian War of Independence, from 1945, to 1949, Yogyakarta served as the capital of Indonesia.
Today, Yogyakarta is the second most important tourist destination in Indonesia (after Bali), as a result of the rich Javanese fine arts and culture found in the area, including batik dyed fabric (a manual, wax-resist dyeing technique), ballet, drama, gamelin music, poetry, silver work, and leather shadow puppet shows (wayang kulit). Yogyakarta is also home to the largest university in Indonesia, Gadjah Mada University.
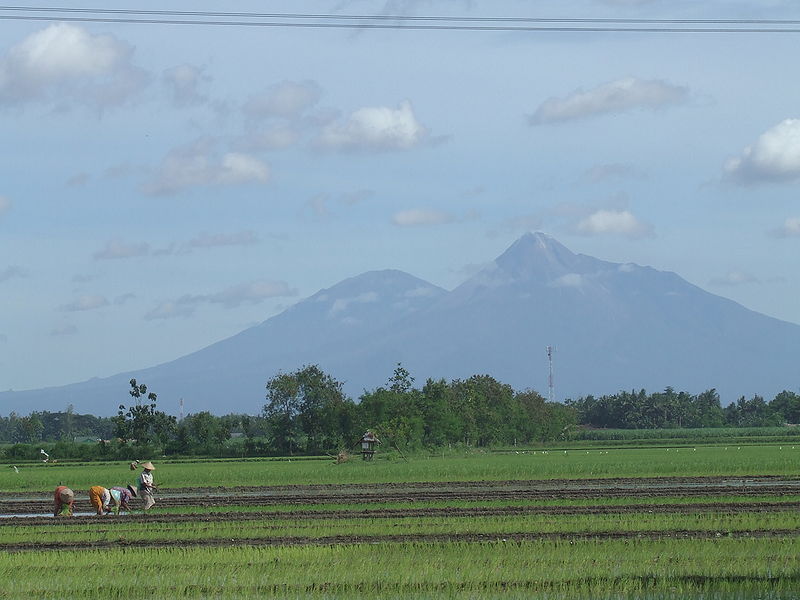

Mount Merapi (left) and Mount Merbabu, about 20 miles north of Yogyakarta. Rice farmers are in the foreground. Courtesy of Wikipedia.
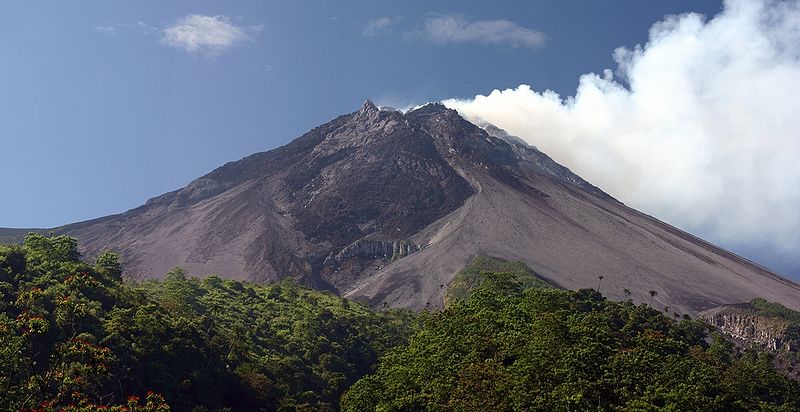

Mount Merapi, elevation 9,738 feet, is the most active volcano in Indonesia. Merapi most recently erupted in November 2010. Courtesy of Wikipedia.
A few more facts about Yogyakarta (climate data from Wikipedia):
- Time zone: Western Indonesian Time (UTC+7)
- Average elevation: 374 feet (114 meters)
- Climate zone: Tropical monsoon
- Average high temperature: 86 °F (30 °C)
- Average low temperature: 71 °F (22 °C)
- Average annual high/low temperature range: 84 to 88 °F (29 to 31 °C) / 69 to 72 °F (21 to 22 °C)
- Average annual precipitation: 86 inches (2,180 mm)
Weather: Yogyakarta is just south of the equator, at just north of 8 °S and just west of 110 °E. Because of its location, the city experiences a tropical monsoon climate. This means the temperature is warm and does not vary much throughout the year, and also means it is a rainy place but there are wet (November – April) and dry (May – October) seasons.
Currently, Yogyakarta is in the rainy season, with highs in the mid-80s, lows in the low 70s, and a chance of rain and thunderstorms every day. Winds are near calm.
Here’s a satellite image from the Meteorological Climatological and Geophysical Agency in Indonesia:
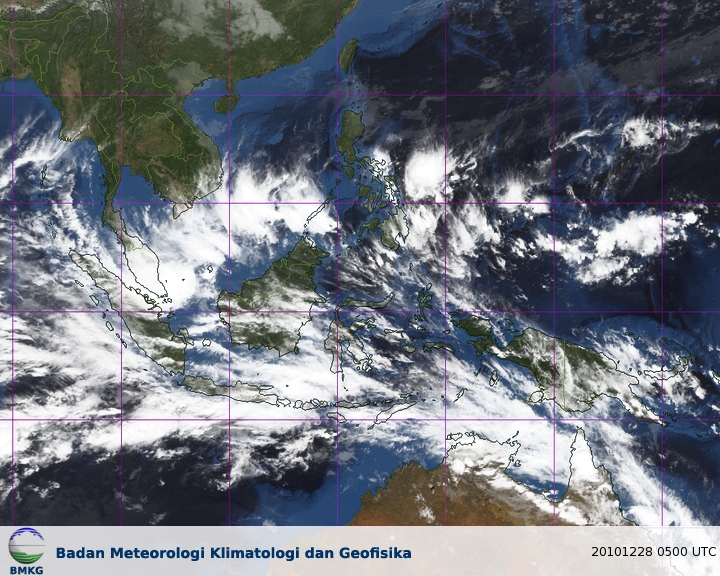
For weather maps and information on current and forecast Yogyakarta weather, see the Meteorological Climatological and Geophysical Agency of Indonesia, Weather Underground, and Weather Online UK.
For more information on Yogyakarta, here’s a link to Wikipedia.
Next Tuesday I plan to take a look at the climate and weather in another part of the globe. As always, if you have any comments or suggestions for future cities, please leave a comment!
Permalink
11.09.10
Posted in Non-US Weather, Weather News at 3:26 pm by Rebekah
This week’s post in the global weather and climate series features Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy.
-
-
-
-
-
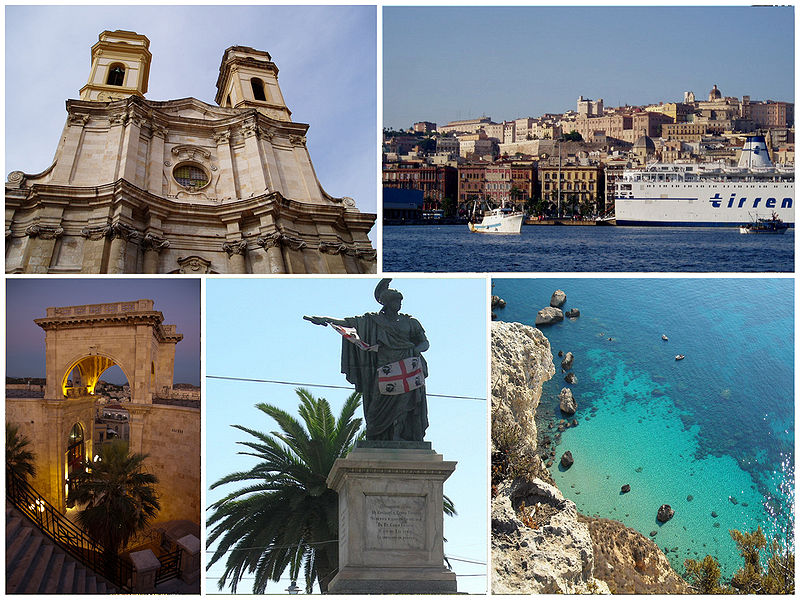

Around Cagliari. Click to enlarge. Courtesy of Wikipedia.
Cagliari is located on the southern coast of Sardinia, an island and Italian province off the western coast of Italy. Cagliari is the capital of Sardinia and is home to nearly 160,000 people (about 400,000 in the metro). This city was established some time in or before the 7th century B.C., between the sea, fertile plains, and mountains. Today, Cagliari has one of the largest fish markets in Italy and tourism is a major part of economy.
A few more facts about Cagliari (from Wikipedia):
- Time zone: Central European Time (UTC+1) or Central European Summer Time (UTC+2)
- Elevation: 13 feet
- Climate zone: Mediterranean
- Average high temperature: 70 °F (21 °C)
- Average low temperature: 53 °F (12 °C)
- Average annual precipitation: 17 inches (426 mm)
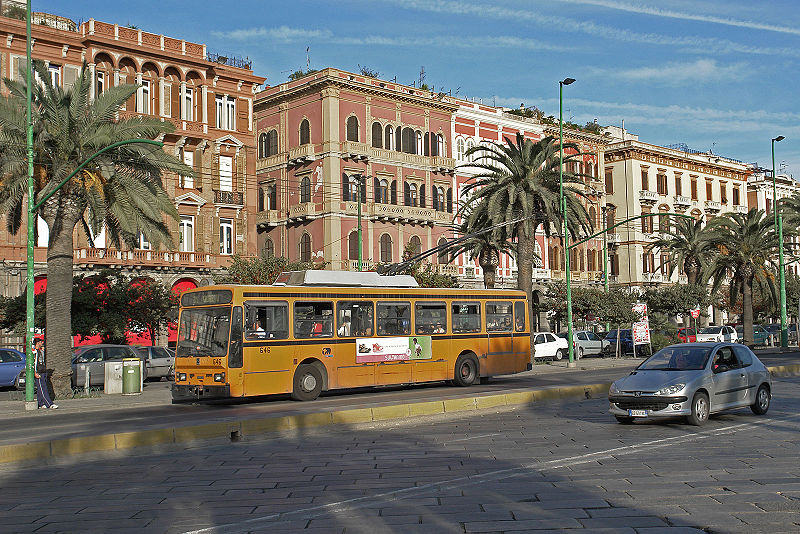

Via Roma in Cagliari. Click to enlarge. Courtesy of Wikipedia.
Current weather: This week in Cagliari, highs are in the mid-60s and lows are in the low 50s. Skies are expected to be mostly clear, after a chance of rain Wednesday night and Thursday night.
With a trough and an associated surface low moving over France today,y there is a decent chance for severe weather (strong wind gusts, tornadoes, and excessive convective rainfall) in Sardinia and across much of the Mediterranean. ESTOFEX, the European Storm Forecast Experiment, has made the following forecast:
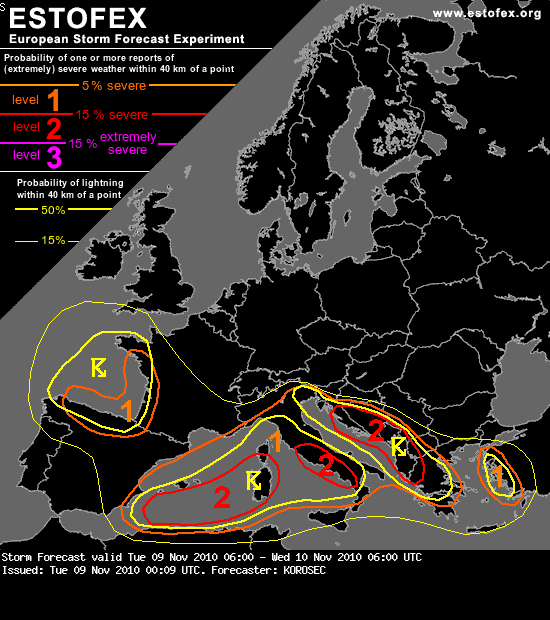
For weather maps and information on current and forecast Cagliari weather, see the Meteo Italia (Italian’s national weather service, in Italian), Weather Underground, and Weather Online UK (maps and models).
For more information on Cagliari, here’s a link to Wikipedia.
Next Tuesday I plan to take a look at the climate and weather in another part of the globe. As always, if you have any comments or suggestions for future cities, please leave a comment!
Permalink
10.19.10
Posted in Non-US Weather, Tropical Weather, Weather News at 8:06 am by Rebekah
This week’s post in the global weather and climate series features Singapore.
-
-
-

Singapore montage, from Wikipedia (click to enlarge).
Singapore is a country made up of 63 islands located at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula. Singapore is located just 85 miles north of equator, thus the country has a tropical climate. The capital city of the country of Singapore is Singapore (the city takes up much of the land area on the main island). The country is 274 mi² with a population of 5.1 million and a population density of about 18,000 per square mile. This makes Singapore third overall in terms of population density, after Macau and Monaco (each with over 40,000 per square mile). Singapore has recently been working on land reclamation, by expanding the size of their islands and joining some islands to make more room for people.
Singapore was first founded in the 2nd century AD, but burned down by Portuguese raiders in 1613. In 1819, Singapore was discovered by the British East India Trading Company, who signed a treaty to use the area as a trading post. Singapore officially became a British colony in 1824, though it was lost to the Japanese in just 6 days in World War II. After Japan surrendered, the British regained the country. Singapore became officially independent in 1965.
Singapore is currently the world’s 4th leading financial center, has the fastest growing economy in the world, and has been ranked with the best quality of life in Asia (and 11th around the world). Tourism is important to Singapore’s economy, though the country most heavily relies on exports and refining imported goods (especially manufacturing). An estimated 42% of Singapore’s population is foreign, and foreign workers make up 50% of the service sector. There are four official languages in Singapore: English (taught in schools), Malay (national language but more symbolic than spoken), Mandarin Chinese, and Tamil.
A few more facts about Singapore (from Wikipedia):
- Time zone: Singapore Standard Time (UTC+8)
- Elevation: 0 to 545 feet
- Climate zone: Tropical rainforest
- Average high temperature: 88 °F (31 °C)
- Average low temperature: 75 °F (24 °C)
- Average annual precipitation: 85 inches (2,150 mm)
The hottest months in Singapore are May and June, with the wettest months being November and December. Relative humidity is often 90% during the morning and 60% in the afternoon. Haze is common from August to October, when smoke from bush fires in Indonesia may affect the country. Occasionally the country may be affected by typhoons, but since Singapore is so close to the equator, most storms would stay well north.
Current weather: Based on the climatology of Singapore, the recent weather is about average. Highs this week are around 90 °F, lows of 77 °F with dewpoints in the mid- to upper 70s (that’s what keeps the temperature from getting lower…it can’t drop below the dewpoint, thus the nighttime humidity could be quite high and miserable). Some rain is expected this week, though the country is not likely to be affected by Typhoon Megi.
A recent reader commented that the humidity in Singapore sometimes goes up when there’s a typhoon affecting Asia. I might first speculate that this has something to do with the wind direction. If the typhoon is, as Megi is, near the South China Sea, then the wind direction over the Malay Peninsula may be from the southwest. However, Singapore is so close to the equator, the winds would not be strong enough to affect moisture in this way.
But if the change in humidity occurs more so before the typhoon draws near land, I could speculate that this may have something to do with the weather pattern that is bringing the typhoon towards Asia. For example, if there’s a ridge of high pressure over eastern Asia (see below…upper level ridge and upper-level winds in black), the surface winds around Singapore may be more from the east (green arrows in figure below). These easterly winds are part of what would push a typhoon towards Asia in the first place. Without knowing a lot about the geography and weather patterns in southeast Asia, I would suspect that an easterly wind would bring increased moisture from the South China Sea. However, the prevailing wind direction is likely from the east anyway, so I’m not sure if this along the right lines or not.
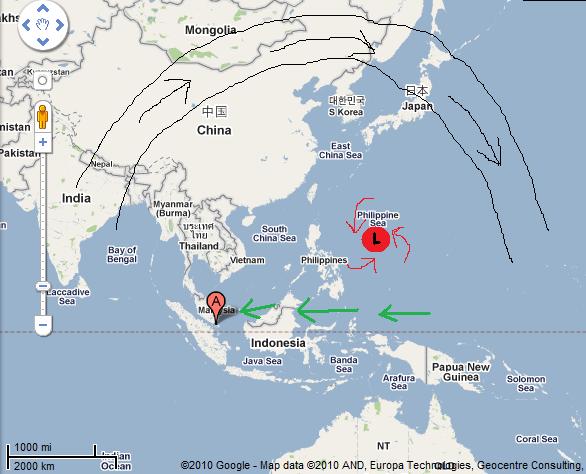
Map from Google Maps. Shows idealized wind patterns in eastern Asia, with upper-level ridge and winds in black, typhoon in red, and easterly surface winds below the ridge in green.
For weather maps and information on current and forecast Singapore weather, see the National Environment Agency (Singapore’s meteorological agency website), Weather Online UK (maps, models, and forecasts for around the world), and Weather Underground.
For more information on Singapore, here’s a link to Wikipedia.
Next Tuesday I plan to take a look at the climate and weather in another part of the globe. As always, if you have any comments or suggestions for future cities, please leave a comment!
Permalink
10.18.10
Posted in Non-US Weather, Tropical Weather, Weather News at 10:29 am by Rebekah
Super Typhoon Megi made landfall in the Philippines early this morning, on the northern end of the island of Luzon. With a reported pressure of 914 mb, Megi was one of the strongest landfalling tropical cyclones on record (Category 5 Dean in 2007 had a landfalling pressure of 905 mb).
Infrared satellite image of Megi at landfall, from Weather Underground:
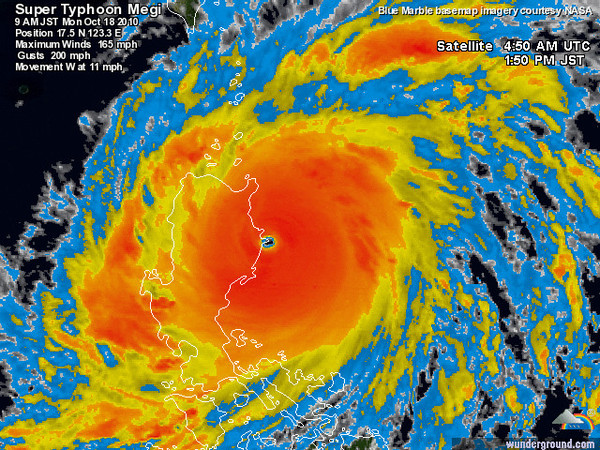
Megi bottomed out just before landfall at 885 mb, the strongest tropical cyclone since Hurricane Wilma in 2005 (882 mb, lowest pressure recorded in the Atlantic basin). Megi’s 10-minute sustained maximum winds peaked at 145 mph…1-minute sustained winds, which are used in the US to determine the ranking on the Saffir-Simpson Scale, peaked at 185 mph. Wind gusts were up to 220 mph.
Different ocean basins have different classification schemes for tropical cyclones, hence the different names. If Megi were in the Atlantic or eastern Pacific, the tropical cyclone would have been classified a Category 5 hurricane. In the waters of the western Pacific, Megi was called a “super typhoon”.
For more information on how tropical cyclones are classified based on ocean basin, see the chart on one of my previous blog entries, “Tropical Cyclone Ului Make Landfall in Australia“.
You may have heard Megi being called “Juan” as well. Megi is the “official” name for the tropical cyclone, but the Philippine Meteorological Service is calling the storm Juan. Different countries are allowed to have their own names for the storms, though the official naming goes to the World Meteorological Organization, who names the storm based on a list of names contributed to by various countries around the western Pacific.
Megi is now the equivalent of a Category 2 on the Saffir-Simpson Scale, but is expected to increase to the equivalent of a Category 4, before decreasing in intensity again and striking the south China coast somewhere just south of Hong Kong.
Weather Underground forecast track map (click to enlarge):
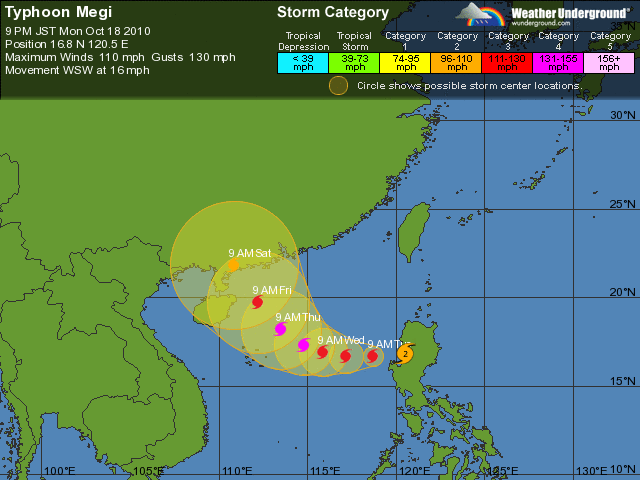
Here’s what Megi looks like right now on satellite, from Weather Underground:
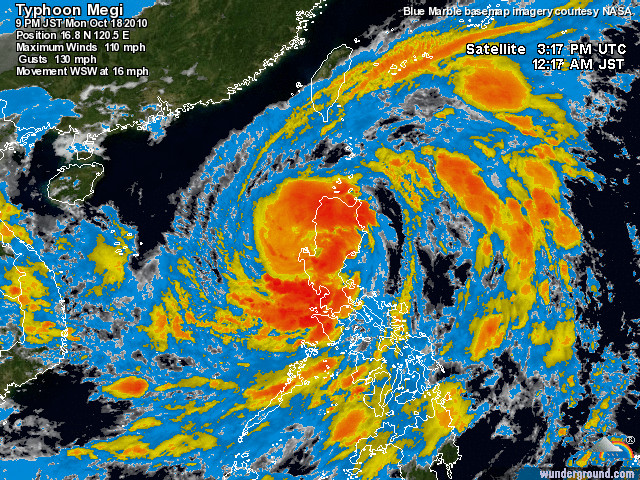
Permalink
10.17.10
Posted in Non-US Weather, Tropical Weather, Weather News at 10:04 am by Rebekah
Super Typhoon Megi, a strong tropical cyclone in the western Pacific basin, is forecast to make landfall in the Philippines (on the big island of Luzon) in less than 24 hours.
As you can see from the Weather Underground forecast track below (click to enlarge), if this tropical cyclone were in the Atlantic basin, it would be classified a Category 5, with winds of 180 mph and gusts to 220 mph (pressure is down to 895 mb). Megi is the strongest tropical cyclone in the western Pacific in nearly 20 years.
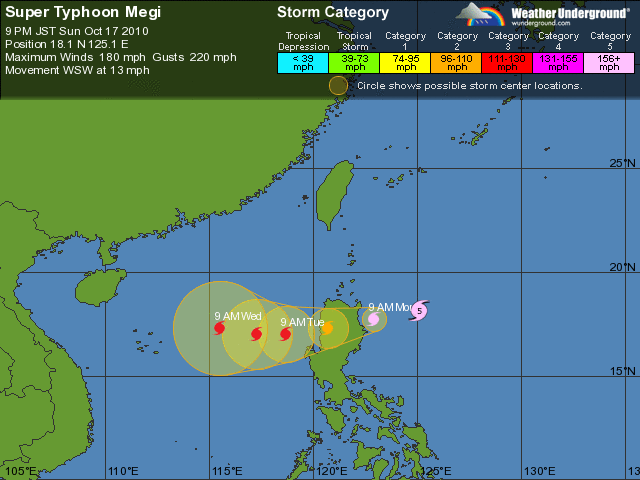
Here’s an infrared satellite image of Megi, again from Weather Underground:
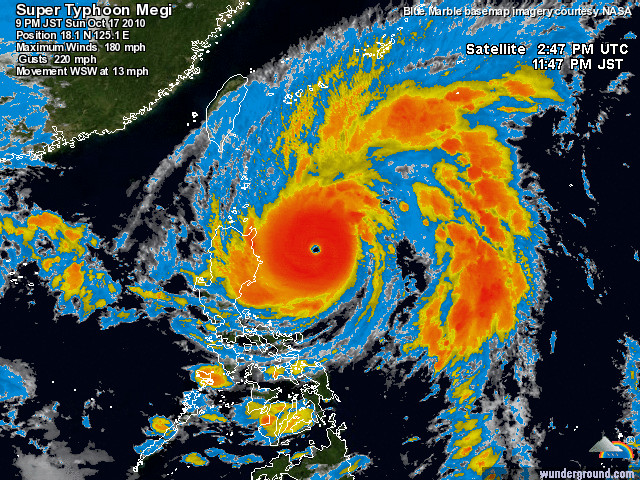
After Megi strikes Luzon as a Category 5, the cyclone will briefly weaken before restrengthening and aiming its sights on southern China.
Permalink
« Previous Page — « Previous entries « Previous Page · Next Page » Next entries » — Next Page »













